Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody Sequencing for Neurodegenerative Disease Research
Rabbit polyclonal antibodies are commonly used reagents across biotech and academia. As of 2024, 43% of commercial catalog antibodies are polyclonals, and 66% of those are rabbit derived. Hyperimmunized rabbits consistently generate high affinity, target-specific immune responses to small molecules, peptides, proteins, and more. They are inexpensive to generate (compared to monoclonal antibodies), making them a popular choice when creating a new detection reagent.
While rabbit polyclonals are popular, there are significant drawbacks.
-
The supply of polyclonal antibody is limited by what the animal(s) can produce. Once an animal is gone, a polyclonal to the same target can be generated in a new animal but there’s no guarantee the new polyclonal will perform as well as the original.
-
The polyclonal antibody is comprised of many different unknown antibody clones, and cannot be fully characterized for the purpose of IP protection.
Rabbit polyclonal antibody sequencing enables the conversion of polyclonal antibodies into recombinant monoclonal antibodies. Once the sequences of the individual antibody clones are recovered, each monoclonal antibody can be expressed, engineered, and validated, creating an infinite supply of identical reagent. In this case study we show how Abterra Bio’s Griffin technology for rabbit polyclonal antibody sequencing rescues a research project focused on developing new therapies for neurodegenerative diseases.
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody to a Progranulin Protein Domain
Dr. Thomas Kukar (lab website) is an Associate Professor at the Emory University School of Medicine. His research focuses on the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases, and the role of the progranulin protein in disease such as Alzheimer’s disease, ALS, and dementia.
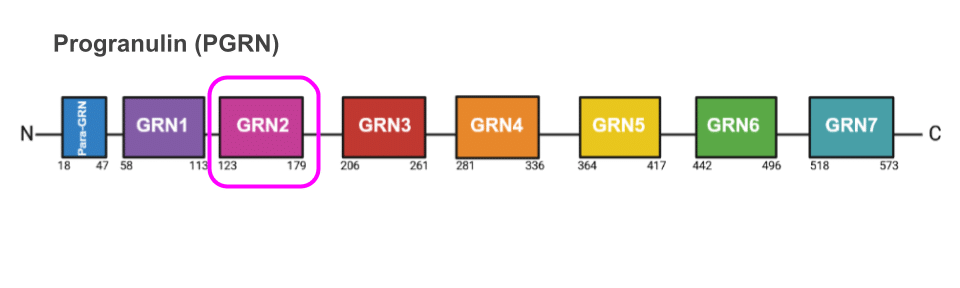
The progranulin protein is comprised of 7 granulin domains.
The Kukar lab had created and validated rabbit polyclonal antibodies that detect subdomains of the progranulin protein. One antibody detected the grandulin 2 domain (GRN2), but supply was running low and a new polcylonal antibody development project would be time consuming. To make matters more challenging, no B cells remained from the immunized rabbits.
Abterra Bio collaborated with Dr. Kukar to create recombinant monoclonal antibodies that recapitulate the activity of the polyclonal. Griffin was used to perform rabbit polyclonal antibody sequencing on the sample.
Griffin Stage 1: Clonality Assessment
The first stage of Griffin evaluates sequencing feasibility by performing clonality assessment. We discussed this stage in more depth in another blog post. In essence, clonality assessment determines the diversity of the polyclonal antibody. If the antibody is too diverse, then accurate sequencing will be challenging, and simplification of the polyclonal antibody is recommended.
In this project, a diverse collect of CDR3s were detected, including two expanded families with multiple related CDR3s. This is often a sign of affinity maturation within those clones.
The network to the right was produced during clonality assessment. Each node is a distinct CDR3 amino acid sequence, and edges are drawn between CDR3s are that are within edit distance 2.
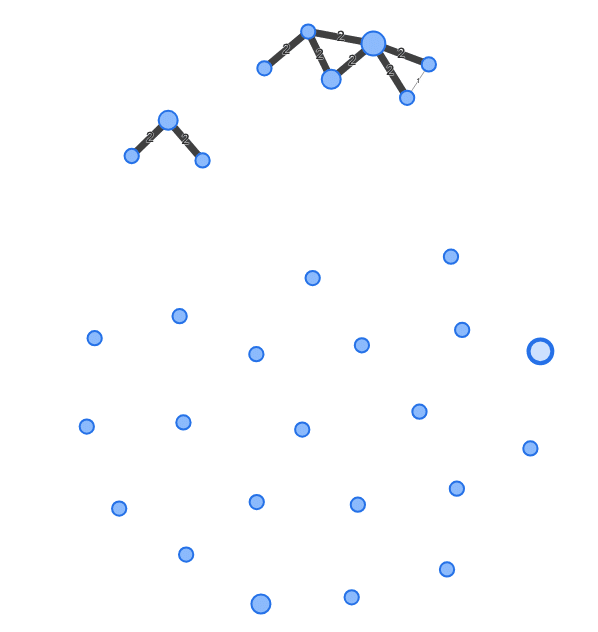
The CDR3 network produced during clonality assessment.
Griffin Stage 2: Sequencing and Assembly
In Stage 2, peptides generated from the polyclonal antibody are de novo sequenced and assembled into full-length antibodies. With Griffin, bottom up and middle down proteomics is used to generate many peptides spanning the entire antibody sequence, and with sufficient length and overlap to enable assembly.
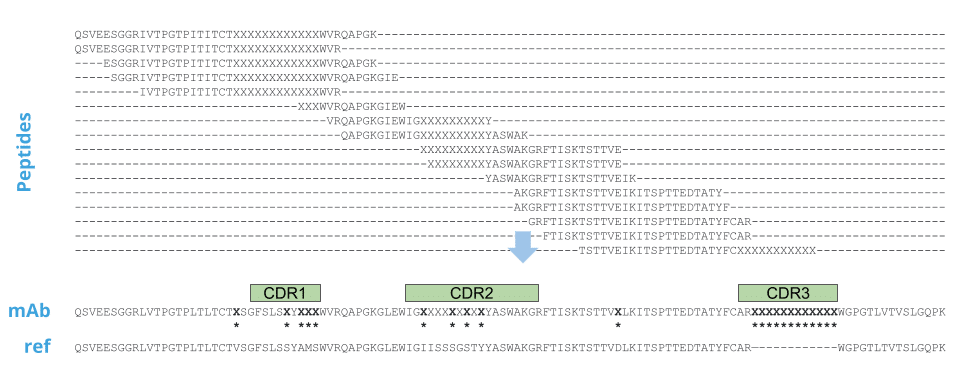
A sample set of peptides are aligned prior to assembly into the final full-length sequence (mAb). The mAb is shown aligned to the closest germline genes (ref) and mutations are noted with *.
For each CDR3 detected in Stage 1, one or more full-length assembles are generated.
Antibody Validation
The assembled variable region sequences were synthesized and cloned into vectors containing rabbit IgG/IgK constant regions. Recombinant antibodies were expressed and purified prior to binding evaluation. The Kukar lab was most interested in using the monoclonal antibodies in ELISA and western blots.
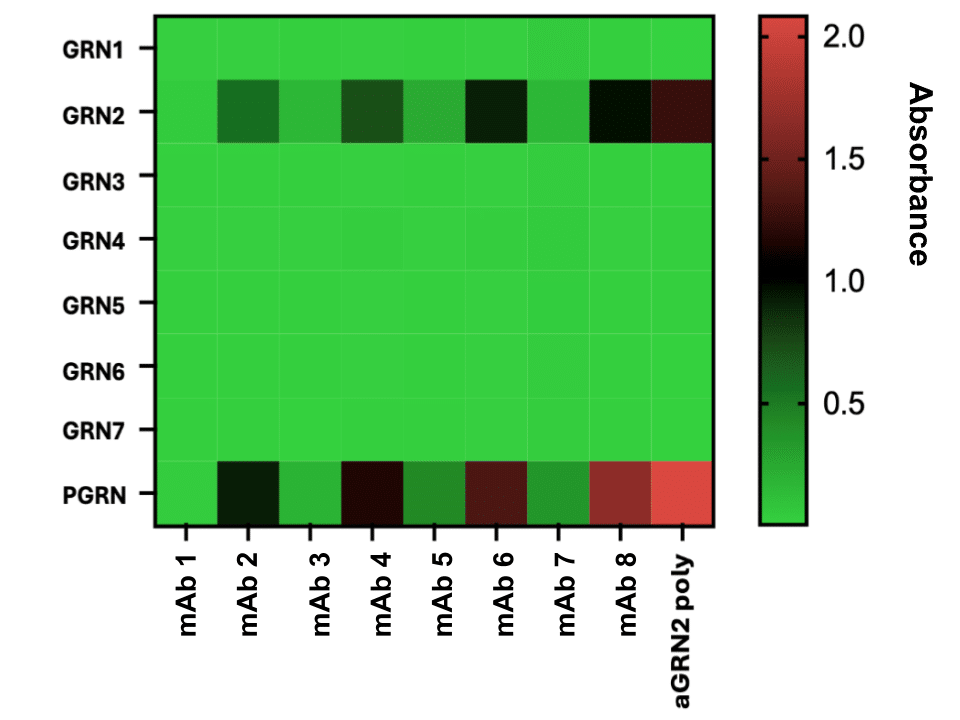
ELISA against recombinant PGRN and GRN domains showed that the antibodies were highly specific to the GRN2 domain as well as the PGRN protein (which contains GRN2)
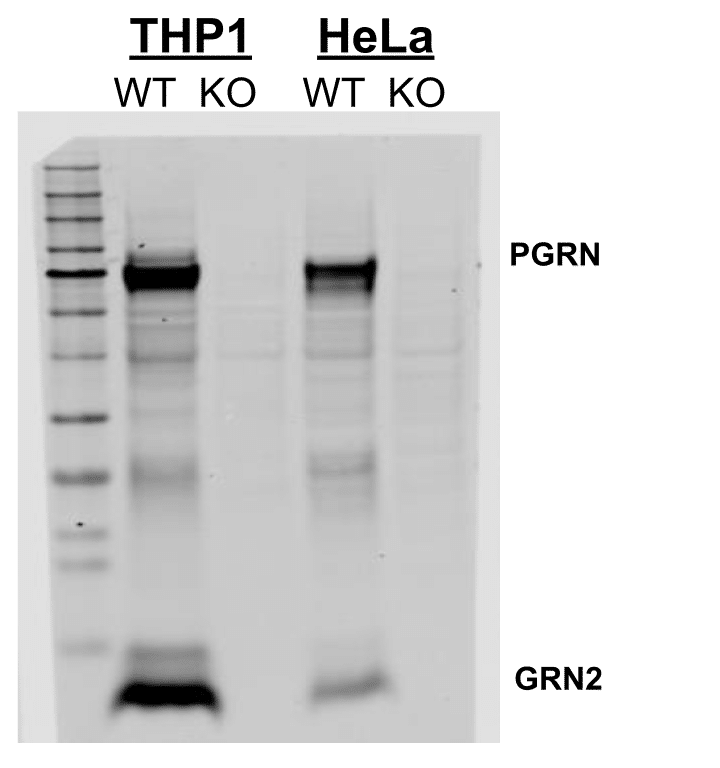
Western blot analysis of two cell lines showed detection of both PGRN and GRN2 by mAb 6, and loss of detection when these proteins were knocked out.
Summary
Rabbit polyclonal antibody sequencing enables to conversion of polyclonal antibodies into recombinant monoclonal antibodies. Recombinant monoclonal antibodies can be easily engineered as well as consistently and perpetually produced.
Want to learn more? Check out these related resources:
- For monoclonal antibody sequencing, Valens is a service built on 20 years of research.
- There are different methods for polyclonal antibody sequencing. We compared the two most common methods in a blog post.
- Watch a presentation about our rabbit polyclonal antibody sequencing method in a talk by our CEO on Abterra Bio’s YouTube channel.
