Advantages of High-Throughput Hybridoma Sequencing with NGS
Having a diverse collection of leads at the beginning of your antibody development campaign is critical for downstream success. As we know well, the immune response to immunization often focuses on a small number of antibody families with highly similar CDR3s which can lead to reduced diversity going into the functional screens. High-throughput hybridoma sequencing gives you more information about your clones at an earlier stage to prevent redundant effort screening duplicate hybridomas and to ensure you don’t miss out on rare, but unique clones.
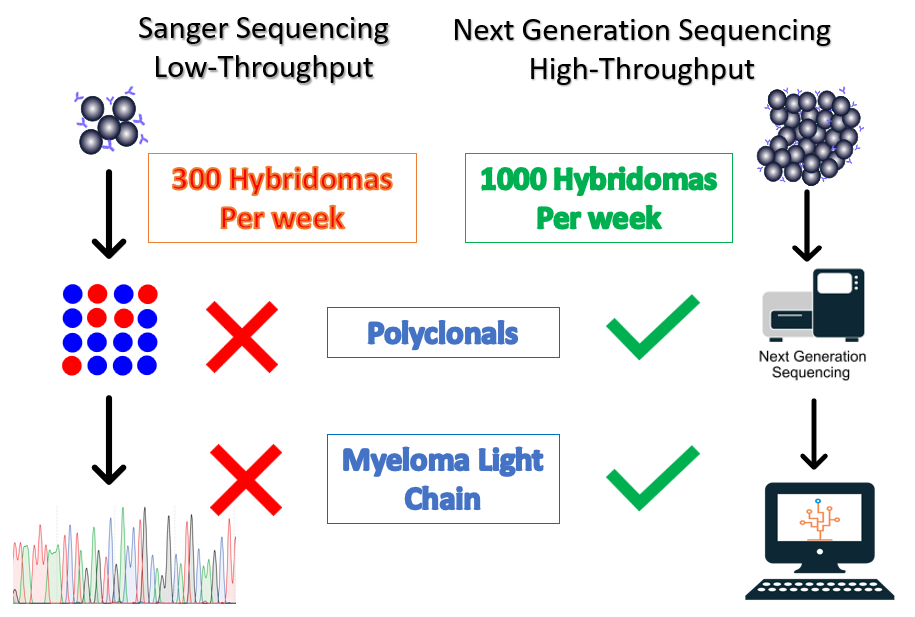
Hybridoma technology is commonly used in the development of therapeutic antibodies and continues to be an efficient source of antibody production. Sanger sequencing is the traditional method for sequencing hybridomas, however, the throughput is unable to keep up with modern hybridoma campaigns. In a typical hybridoma campaign, thousands of clones are screened. Sanger sequencing equipment can typically process 96 samples (heavy or light chain) at a time in a day. It would take almost 3 weeks to sequence one thousand clones.
In a recent study, a third of hybridomas were found to be polyclonal and the myeloma cell line used for fusion can also express its own antibody unrelated to the antibody of interest[1]. This presents a significant challenge for Sanger sequencing. In contrast, next-generation sequencing enables our Reptor hybridoma sequencing workflow to sequence 1,000 hybridomas, even polyclonals, per week.
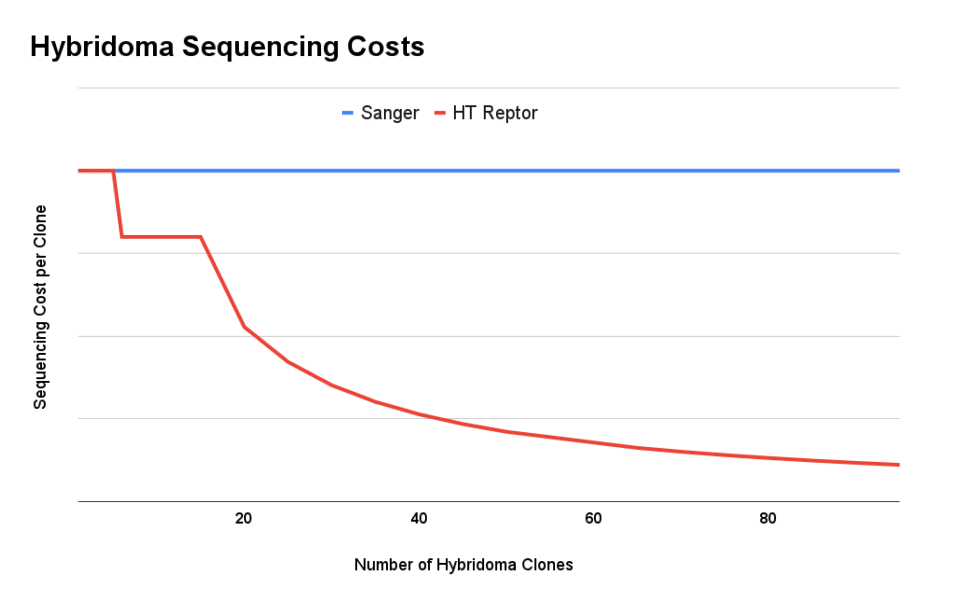
The high-throughput nature of next generation sequencing creates significant economies of scale. Whereas sequencing clones one by one can cost ~$1,000 per hybridoma, our high-throughput process with Reptor can deliver high-quality sequence information for as little as $200/clone. Each clone is sequenced by multiple reads, which means that Reptor can recover low-frequency variants present in polyclonal samples.
At Abterra Bio we use NGS for a variety of applications to support antibody discovery.
-
We used NGS to build clonal trees for our hybridoma hits and evaluate clonal diversity during the hybridoma process.
-
We assessed the affinity of relatives of our VHH hits using hit expansion.
-
We evaluate repertoire characteristics across different species and different isotypes.
We’ve sequenced thousands of hybridomas and our experience means more high-quality sequences in your hands.
-
Over 10,000 hybridomas sequenced
-
All major species sequences including wild-type mouse and rat strains as well as commonly used transgenic rodents.
-
Hybridoma sequencing uses the same validated platform that we use to sequence hundreds of thousands of antibody sequences in bulk immune repertoires.
References:
[1] Bradbury ARM, et al. When monoclonal antibodies are not monospecific: Hybridomas frequently express additional functional variable regions. MAbs. 2018 May/Jun;10(4):539-546. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2018.1445456. Epub 2018 Mar 29. PMID: 29485921; PMCID: PMC5973764. (Europe PMC)
Related Posts
VHH Antibody Repertoire to Phage Library Comparison
Project Summary Camelids such as llamas and alpacas produce conventional antibodies as well as heavy-chain only antibodies (HCAbs) from which the small, stable antigen-binding domain (VHH) can be extracted. Abterra Biosciences developed Reptor, a proprietary antibody...
Case Study: Reptor Biological vs Technical Replicates
Project Summary Next-generation sequencing of B cell populations (Rep-Seq) has become a powerful tool in immunology and antibody discovery. At Abterra Bio we developed Reptor, an integrated Rep-Seq sequencing and analysis service. A key goal of Reptor is to provide...
Abterra Opens Its Doors To Celebrate New Location With Open House
Celebrating milestones is an important part of our personal and professional journeys. We wanted to commemorate this exciting new chapter in Abterra's story with the people who mean the most to us: our devoted employees, cherished families, esteemed investors, and...