Case Study: Alicanto Discovers High Affinity Rabbit Antibodies to Detect Neurofibromin
Researchers at Infixion Bioscience are on a mission to develop new therapeutics for the “orphan disease” neurofibromatosis type 1, which is diagnosed at a rate 1 in 3000 live births, impacting millions across the globe. Neurofibromatosis type 1 is a genetic disorder that results in tumor formation on nerves and can lead to a wide range of symptoms from learning disabilities to malignant tumor growth. The disease is associated with mutations in the gene NF1, which lead to expression of an aberrant form of neurofibromin (NF1) protein.
Current commercial reagents for NF1 show polyreactivity and/or low affinity. Infixion Bioscience and Abterra Biosciences set out to develop high affinity antibody reagents to detect NF1 for use in western blot, ELISA, and immunohistochemistry assays.
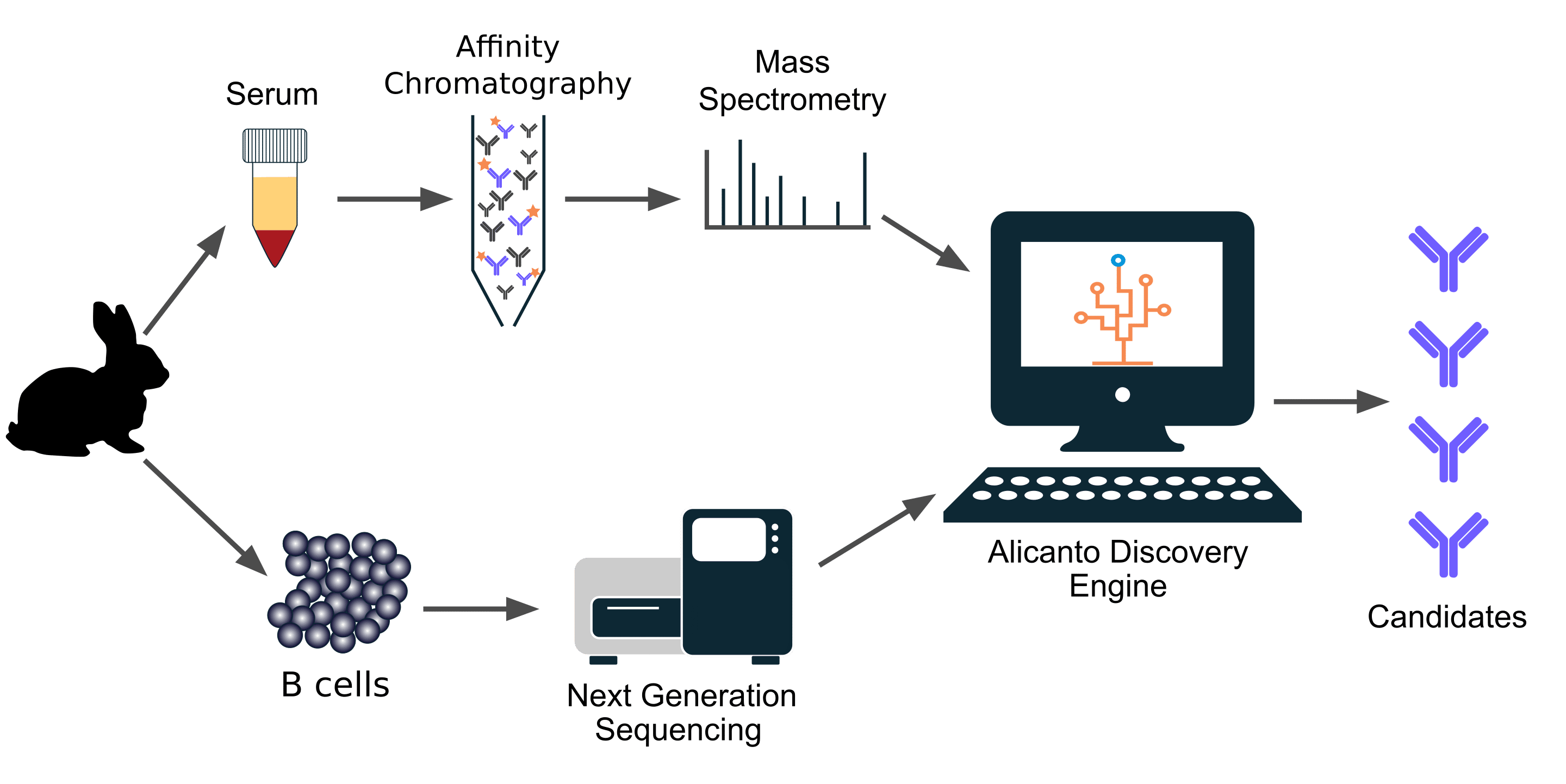
Alicanto® Workflow
Abterra Biosciences has developed Alicanto®, a technology for discovering antibodies directly from serum. In this project, two New Zealand white rabbits were immunized with full-length, recombinant human NF1 isoform 2 (without Exon 23a). Samples from the rabbits were analyzed by Alicanto as follows:
- Proteomics: Anti-NF1 antibodies were enriched from the serum of the rabbit with the highest response to NF1. Antibodies that targeted the His-tag on NF1 were removed using a second affinity column. The affinity purified antibodies were analyzed by tandem mass spectrometry.
- Genomics: Throughout the immunization, samples were collected to obtain B cells. These samples included peripheral blood, spleen, and bone marrow. Each sample was analyzed using a bulk B-cell sequencing pipeline. From the next-generation sequencing data, Alicanto constructed a large database of antibody sequences expressed by the rabbit during immunization.
- Data analysis: The mass spectrometry data was mapped to this database to identify candidate antibody sequences that have high affinity to NF1. Candidate selection is performed by a proprietary model that evaluates the next-generation sequencing and mass spectrometry evidence for each sequence and selects the most likely sequences for heavy chain and light chain.
Alicanto® Results
In total, 22.8M sequencing reads were generated, resulting in an antibody sequence database containing 202,148 heavy chain sequences clustered into 24,686 families, and 428,690 light chain sequences clustered into 49,375 families. The mass spectrometry data revealed 27 heavy chain families and 13 light chain families present in the affinity purified antibody sample. Candidates were selected to maximize diversity and to sample from several families.
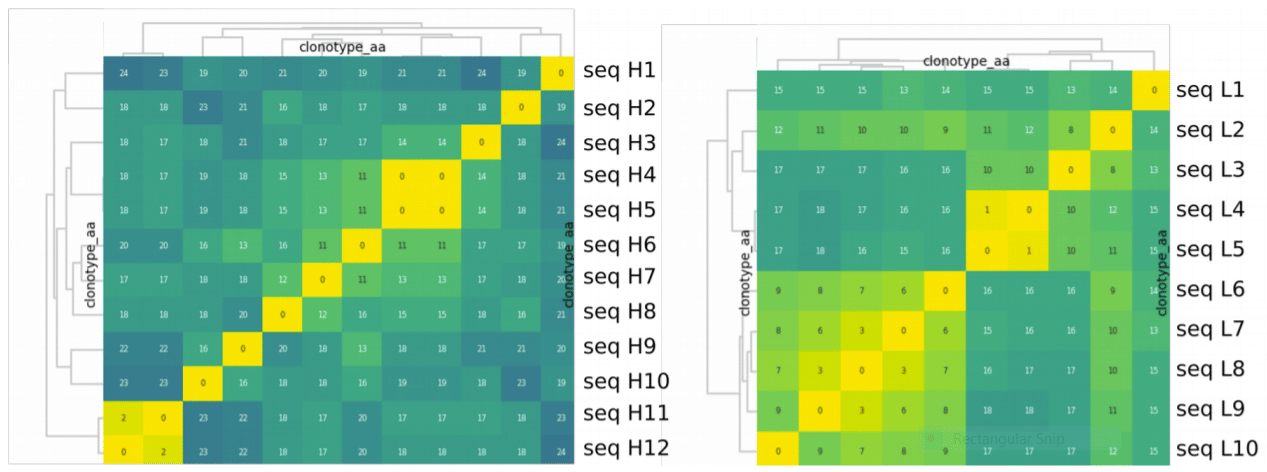
Figure: Clustered heatmaps of the selected candidates (heavy chain on left, light chain on right). The values of the heat map cells show the number of amino acid differences across candidate antigen-binding domains. The heavy chain sequences display greater diversity than light chains.
In total, 12 heavy chain sequences and 10 light chain sequences were selected by Abterra Biosciences. A total of 120 sequence combinations were selected for gene synthesis, recombinant expression, and ELISA screening for binding to NF1
Conclusion
Ultimately, 9 showed reactivity to the target in ELISA. Additionally, two of the antibodies detect NF1 in western blot with better specificity than commercially available antibodies, and two antibodies can be used in a sandwich ELISA for detection of NF1 in native conformation.
Research into the rare disease neurofibromatosis type 1 has been hindered by a lack of tools to detect NF1 expression. Infixion Bioscience researchers are now able to better understand this complex disease using new monoclonal antibodies that are specific and high affinity.
Related Posts
VHH Antibody Repertoire to Phage Library Comparison
Project Summary Camelids such as llamas and alpacas produce conventional antibodies as well as heavy-chain only antibodies (HCAbs) from which the small, stable antigen-binding domain (VHH) can be extracted. Abterra Biosciences developed Reptor, a proprietary antibody...
Case Study: Reptor Biological vs Technical Replicates
Project Summary Next-generation sequencing of B cell populations (Rep-Seq) has become a powerful tool in immunology and antibody discovery. At Abterra Bio we developed Reptor, an integrated Rep-Seq sequencing and analysis service. A key goal of Reptor is to provide...
Abterra Opens Its Doors To Celebrate New Location With Open House
Celebrating milestones is an important part of our personal and professional journeys. We wanted to commemorate this exciting new chapter in Abterra's story with the people who mean the most to us: our devoted employees, cherished families, esteemed investors, and...
Get In Touch